The Bad Request error 400 in Google Chrome indicates that the server was unable to understand or process the request sent by browser.
What Causes Bad Request Error 400 On Google Chrome?
Error 400 is a client-side error that occurs as a result of invalid requests, syntax errors, or routing issues. Additionally, this can occur if the URL is not recognized or you typed it incorrectly. Therefore, double-check that you typed the URL correctly.
Well, In rare cases, bad request errors may also indicate that a server-side problem is preventing your request from being processed. In this case, you can contact the website’s owner to check whether they are aware of the problem, but only after you have exhausted all of the solutions in this guide.
Solution:- How To Fix A 400 Bad Request Error?
1. Clear Your Browser Cache
Clearing the cache and cookies in Chrome can assist you in resolving bad request errors. In addition, when you visit different websites, your browser saves temporary files and various scripts in order to speed up the subsequent load of the respective websites.
However, these files may clog your browser or become corrupted, resulting in a variety of browsing issues, including error 400.
Well, To clear your Google Chrome cache and cookies, follow these steps:
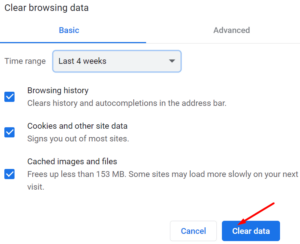
1- Click the menu icon, click History, and then click it again.
2- After that, choose Clear browsing data
3- Check that you have selected all three options for deleting your cache, cookies, and History.
4- After that, select a time period and click the Clear data button.
Restart your computer and check to see if you are now able to access the website that caused the error 400. If the bad request error continues to occur, restart your modem and router and retry.
2. Refresh Your DNS
Chrome has its own internal DNS cache, which you can clear using the following steps:
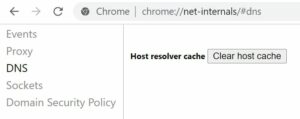
1- Open the browser, and in the address bar, type chrome://net-internals/#dns → press Enter.
2- To refresh the DNS cache, click the Clear host cache button.
3- In the address bar, type chrome: //net-internals/#sockets
4- Click Flush socket pools and then select Close idle sockets.
Well, Close the browser and reopen it to check that this solution worked.
Following that, if you’re using Windows, you’ll need to flush your computer’s DNS using the Command Prompt:
1- In the search bar, type cmd.
2- Right-click Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator → hit Enter.
3- Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter to clear the DNS cache on your computer.
3. Disable Your Extensions
Certain extensions may obstruct your browser’s operation by instructing servers to interpret your browser requests as incorrect or invalid.
We recommend disabling all browser extensions to check if this resolves the Chrome bad request errors.
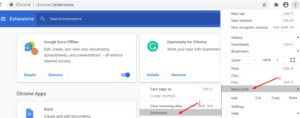
Select Extensions from the menu bar by clicking on the menu icon. Select each extension and turn them all off individually.
4. Additional Solutions
- Create a new Chrome profile.
- If you’re receiving the error 400 bad requests on a specific website, contact the website’s owner via the contact page and inform them of the issue.
- Switch to another browser.
We hope that one of these solutions was successful in resolving your problem.