Fix WiFi Connected But No Internet Access: When you receive the WiFi connected but no internet access problem, it’s frequently a perplexing and dreaded time. It could be a problem with your operating system’s configuration or even with your Router. We’ve frequently seen this ‘No internet on connected WiFi issue’ over the years and have finally put up a step-by-step guide to assist you in resolving this issue.
Where To Look?
If you are experiencing network problems, there are often two places to look:
1- Router
2- The Device Itself
Well, If the Internet is not working on all devices connected to the network, there is a possibility that your Router/Modem is malfunctioning. Additionally, you can inspect the ADSL cable to determine if it is broken or twisted.
Well, If the Internet is not working on a single device, there is a good probability that there is a problem with the device’s WiFi adapter, preventing the device from talking with the Router. The following are nine procedures to fix the WiFi connected but no internet problem.
How To Fix WiFi Connected But No Internet Access Error
1. Restart Device
I get how it sounds, and most of you have probably already done it a couple of times, but if you haven’t, you should.
Rebooting the network devices forces them to update their IP tables and reload their configuration files. Next, both the Router and modem should be turned off (in case you have one). After that, wait 30 seconds before restarting them. Additionally, you should restart your computer to ensure that everything is clean. Finally, after all devices have been reset, retry connecting to see if it works.
2. Check Modem Lights
It is possible that the problem is with your internet connection rather than the devices connected. To confirm, check the Router’s WAN light to make it is blinking. Also, make that the WAN light is not always on or fully off.
In most circumstances, the DSL indicator lights should be ON or green, and the WiFi indication lights should flash. If you’re unsure how to check, contact your ISP’s customer support department to confirm the current internet issue. Also, inquire about the time required to fix the problem.
3. ISP Is Down
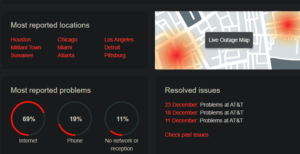
Utilize your mobile data to access Downdetector and search for your ISP. For example, assume it is AT&T. You may use this page to check up the most prominent Internet service providers and search whether their servers are down or experiencing an outage. This convenient service keeps track of coverage worldwide and allows you to check it based on your location.
To determine whether it is down in your part of the world, click on the Live Outage option. A quick search on social media sites such as Twitter may also assist in determining whether other users are experiencing similar troubles where WiFi is connected, but no internet is available.
4. Antivirus Or Other Security App
Well, In the past, antivirus software has been known to cause internet connectivity issues. So, temporarily disable your antivirus and other security apps such as malware to see if this addresses the WiFi connection but no internet error. If that is the case, you now know where to look next. If not, continue to the next step.
At this time, I would also urge that you run a full or comprehensive antivirus and Malwarebytes scan to make you are not infected with anything malicious that is causing this problem.
5. Use Built-in Troubleshooter
If the Internet is working properly on the ISP’s end and on at least one of the connected devices, the problem is most likely with the WiFi adapter. This is readily rectified with the built-in troubleshooter included with Windows and Mac computers.
Select ‘Troubleshoot problems’ from the context menu of the network icon on the taskbar. Windows will automatically scan for and fix network problems. If it is unable to fix the problem, it will at the very least inform you of the issue. You may either conduct an online search for the solution or post a question in the comments section below.
6. Flush DNS
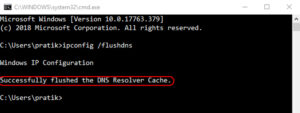
A DNS cache dispute can occasionally result in a WiFi connection but no internet access problem. You can flush DNS to ensure that it is not causing issues. To open Command Prompt with administrator rights, navigate to the Windows start menu and type ‘cmd.’ To flush the DNS, enter the following command and press enter.
ipconfig /flushdns
Here are some additional Command Prompt commands that may assist in resolving WiFi and other network connectivity issues.
Reset the files that Windows uses to connect to the Internet:
netsh winsock reset netsh int ip reset
Set your old IP address to expire and a new one to be assigned automatically.
ipconfig /release ipconfig /renew
If this doesn’t work, issue the following commands sequentially.
ipconfig/flushdns nbtstat -R nbtstat -RR netsh int ip reset c:\resetlog.txt netsh winsock reset
7. Change Wireless Mode On Router
Well, This is a rare case and only occurs if you have an older WiFi card or device installed. However, if you are connecting your PC to the Internet via an ethernet cable, there is a good probability that there is a communication barrier between these two devices. And one method to fix that is by changing the WiFi mode.
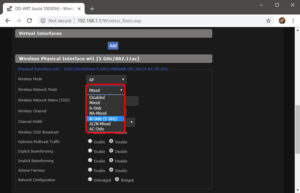
A router supports a variety of wireless modes. For example, you may have seen anything like — 802.11 b or 802.11 b/g or 802.11 b/g/n, or something similar. The terms b, g, n, and ac refer to distinct wireless standards. Typically, the wireless mode is set to 802.11 b/g/n, which is sufficient for the majority of users. Occasionally, older devices, such as cellphones, are incompatible with this mode, resulting in network problems.
Log in to your Router’s dashboard and seek the option labeled ‘Wireless Mode.’ Well, It should be under the Wireless settings, where you set the SSID and password for the WiFi network. Save adjustments after selecting 802.11 b from the drop-down option next to Wireless Mode. Restart the WiFi and check to see if this resolves the problem. If this does not work, try 802.11 g. Also, check to see if the WiFi is connected, but there is no internet access fault that has been fixed.
8. Obtain IP And DNS Automatically
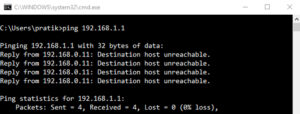
Can the same computer/smartphone connect to a different WiFi network? To check, use a mobile hotspot. This could be caused by a DNS or IP address conflict. Another approach to check this is to use the command line to ping your Router. If you receive a timeout answer or the destination host is unavailable, an IP address conflict is most likely the cause.
Open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges and give the following command:
ping 192.168.1.1
To ensure conflicts, you should set network settings to automatically receive the IP address and DNS settings from the Router. Occasionally, though, setting your devices a static IP address or changing the DNS server helps fix the WiFi connected but no internet connection problem.
The methods below outline how to modify the IP settings in Windows.
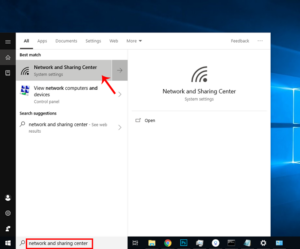
On Windows, we must modify the network adapter settings in order for the computer to receive an IP address automatically. To do so, click on the Start menu and find the Network and Sharing Center.
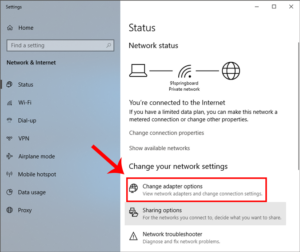
Click on Change Adapter Options once the network window has opened.
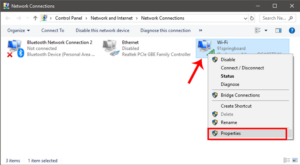
Right-click on your current network adapter or WiFi in the Network Connections box and select Properties.
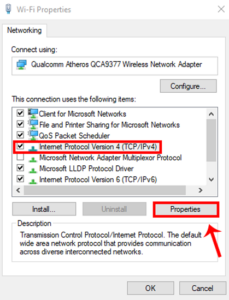
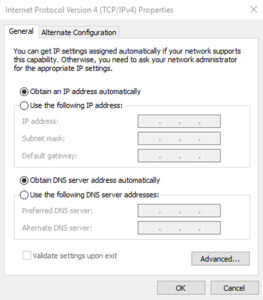
Next, Choose Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) from the pop-up menu and then click Properties.
Select Automatically obtain an IP address and Automatically obtain a DNS server address and click OK to save changes.
You should connect automatically; if not, restart your computer to enable automatic IP address configuration.
9. Fix Network Driver Issues
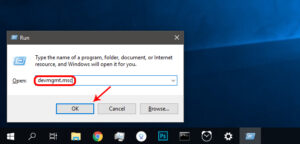
Occasionally, a faulty network driver can lead to poor internet performance. To open Device Manager, press Window+R and type ‘devmgmt.msc’.
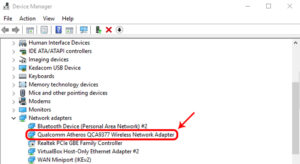
Find your Wireless Network Adapter by expanding Network adapters. Regardless of the brand, it should be suffixed with ‘Wireless Network Adapter.’ Right-click the network adapter and click ‘Update drivers’ from the context option.
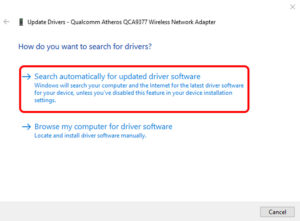
You will now be presented with two options. You can either manually or automatically update the driver (online). First, connect your computer to your Router via an Ethernet wire. If there’re no issues with the Router or internet connection, you should be able to connect without a problem. Once connected, click “Search automatically for updated driver software,” and Windows will find and install the appropriate driver automatically.
If you are unable to connect, you will need to manually download and install the latest driver from the manufacturer’s website using another internet-connected device. Once you’ve downloaded the latest driver, you can manually install it by selecting the “Browse my computer for driver software” option.
10. Reset Router
This option is capable of resolving any router-related issue. Here, You can reset the Router to factory settings to erase any new configuration modifications that may have caused the problem. This also implies that you will need to re-password protect your Router and adjust the default settings to suit your needs.
Although you can reset the Router via its settings, a more convenient method is to press the Router’s physical reset button. Unfortunately, the reset button is typically concealed within a tiny hole, so you’ll need to carefully inspect the Router to locate it. Once located, press and hold the button for 5-15 seconds, or until all lights flicker and the router restarts, using a paper clip or mobile SIM tray opener. When the router restarts, you should be able to connect to the Internet.
11. Reset Your Network
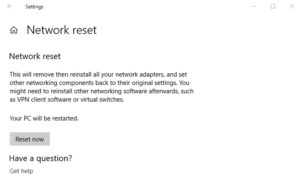
As the name implies, “Network Reset” disables and then reinstalls the network adapter, as well as other networking components. As a result, Windows will forget about your Ethernet, WiFi, and VPN connections, among other things. This is why network resets should be used as a last option.
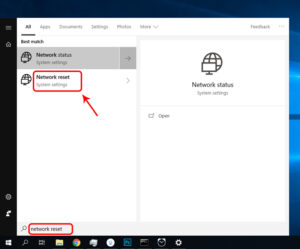
To do so on Windows, open the Start Menu and type Network Reset in the search box.
Well, A new window will open, informing you of the consequences of resetting your network. To continue and restart your computer, click the “Reset now” button.
12. Call The ISP
Finally, it is your Internet Service Provider’s time to ensure that you are always connected to the Internet, especially if they provide the Router and modem. If none of the preceding suggestions worked, contact your ISP and call the exact nature of the problem. They should be able to fix on-call assistance in resolving the problem. If they’re unable to fix the problem over the call, you can request that a representative physically inspect the device.
Conclusion: WiFi Connected But No Internet Access
There is no one-size-fits-all problem with the WiFi connection but no internet connection issue. The aforementioned tips should fix the majority of software-related issues. If, on the other hand, there is a hardware problem — such as a damaged network card or Router — you will need to contact a technician.